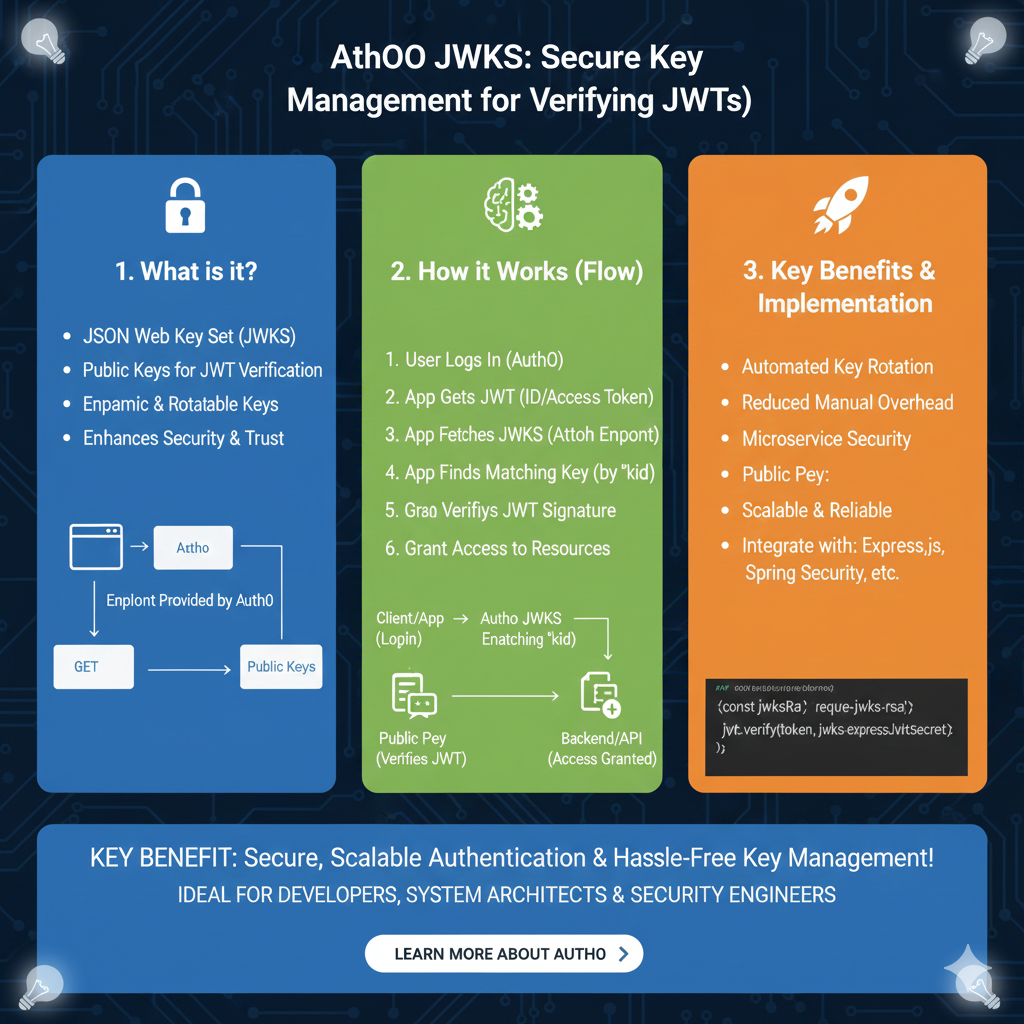
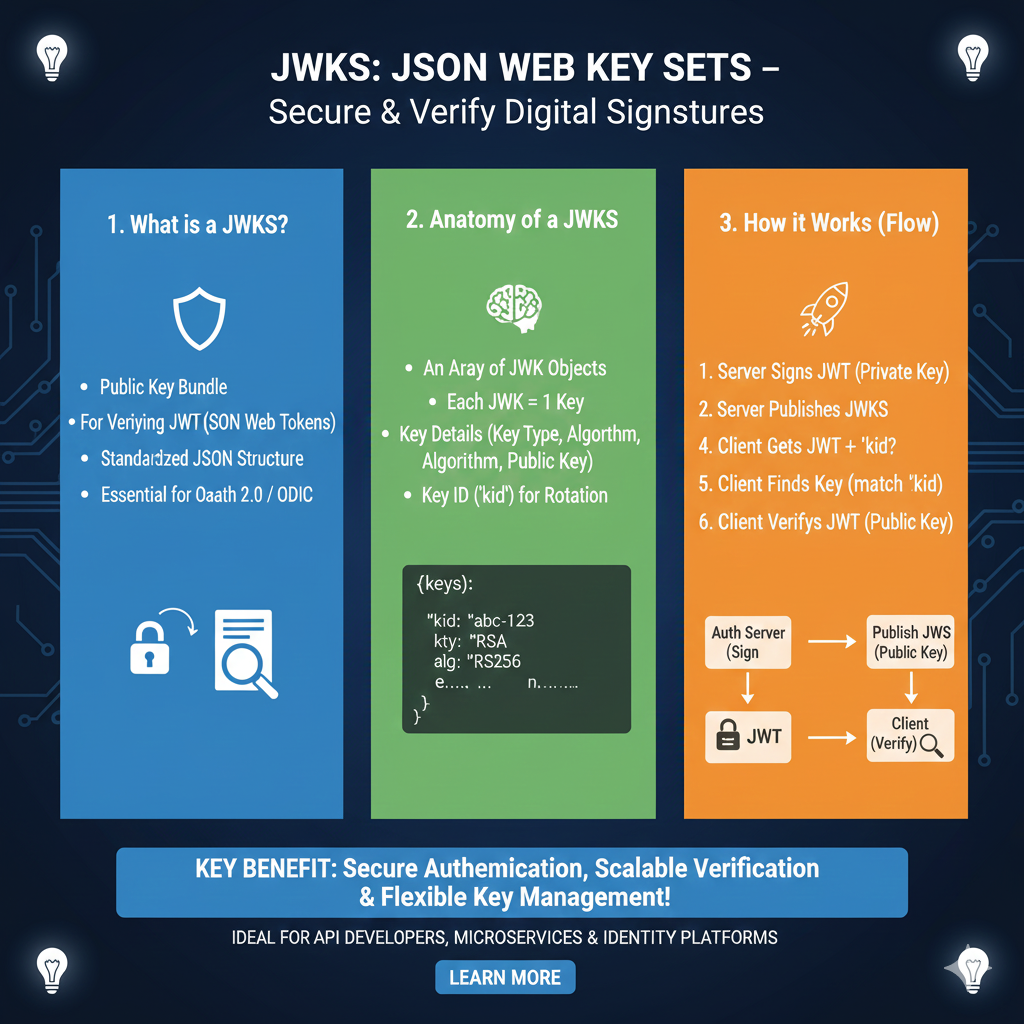
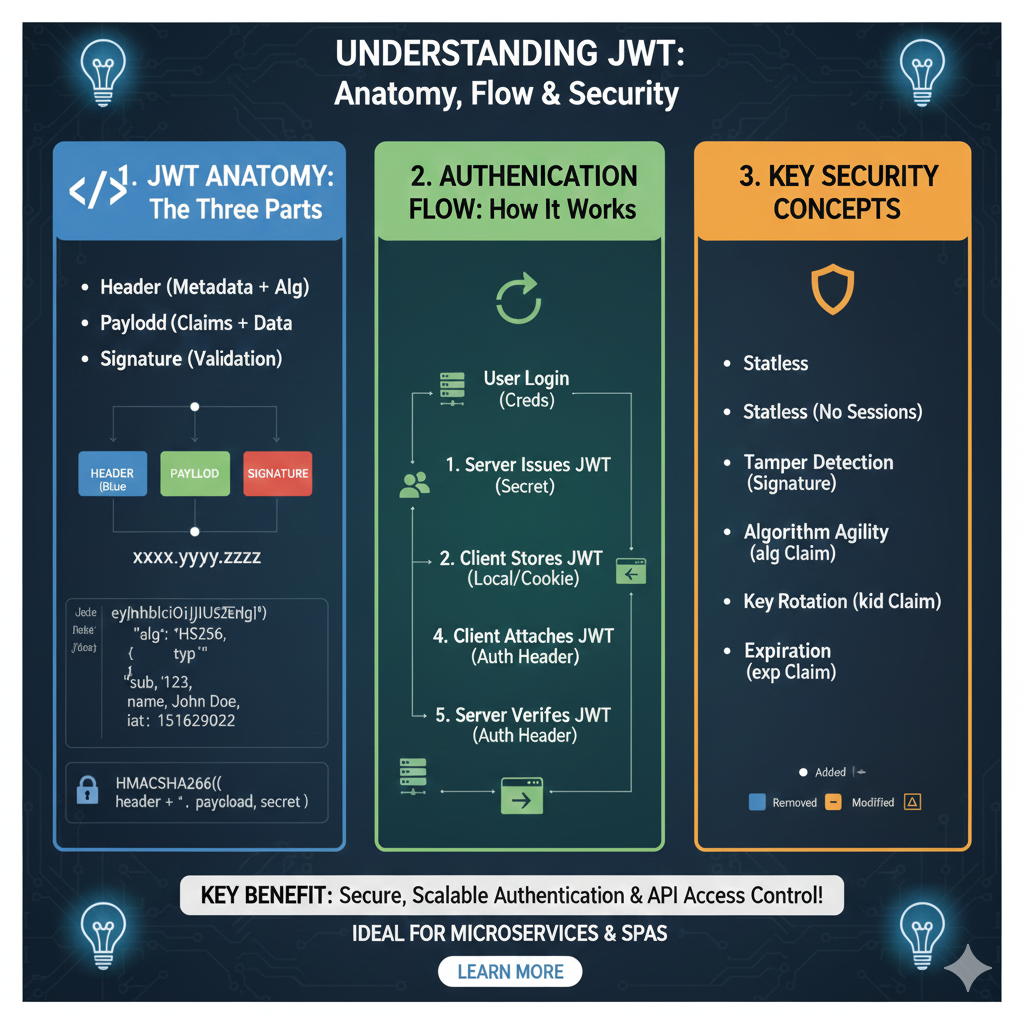
Integrating json web tokens is a standard for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. In a modern node.js application, building a robust jwt authentication system is straightforward thanks to the jsonwebtoken npm package. This guide will walk you through how to generate json web tokens, decode jwt tokens, and manage secure access using the most popular npm package in the nodejs ecosystem.
What is jwt and Why Use the jsonwebtoken npm package?
A jwt (JSON Web Token) is a compact, URL-safe means of representing claims. When you implement jwt npm solutions, you benefit from:
- Stateless Authentication: No session storage is needed on the server, making your nodejs app highly scalable.
- Secure Implementation: Digital signatures ensure jwt tokens cannot be tampered with.
- Standardized Workflow: Using the jsonwebtoken package allows for consistent jwt verify and jwt sign operations across your node js environment.
Step 1: Install the jsonwebtoken npm Package
To begin your implementation, initialize your project and use npm to fetch the necessary library.
Bash
npm init -y
npm install jsonwebtoken
The jsonwebtoken npm package is the “gold standard” for jwt authentication in node js, providing built-in support for various algorithms and issuer validation.
Step 2: How to jwt sign and generate json web tokens
The jwt sign method is used to create a new token. You need a jwt payload (the data), a secret key, and optional settings like the signing algorithms.
JavaScript
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const secret = process.env.JWT_SECRET || 'your_super_secret_key';
const payload = { userId: '12345', user: 'john_doe' };
// Use jwt sign to create the token
const token = jwt.sign(payload, secret, { expiresIn: '1h', algorithm: 'HS256' });
console.log('Generated JWT:', token);
When you sign a token, you are effectively creating a secure “passport” for the user that the node.js application can later verify.
Step 3: jwt verify and validating jwts
When a request comes in, your server must verify the token to ensure it is valid and hasn’t expired. This involves checking the signature against your secret key.
JavaScript
jwt.verify(token, secret, (err, decoded) => {
if (err) {
return console.error('Verification failed:', err.message);
}
// The decoded payload contains the original user data
console.log('Decoded Payload:', decoded);
});
Using jwt verify ensures that only authorized users can access protected resources. If you ever need to inspect a token’s contents manually during development, a jwt debugger like jwt.io is an essential tool.
Step 4: Implementing jwt authentication as express middleware
In a real-world node js app, you typically validate jwt tokens via express middleware. This intercepts the request, checks the header, and processes the decoded data before reaching the final route.
JavaScript
const authenticateToken = (req, res, next) => {
const authHeader = req.headers['authorization'];
const token = authHeader && authHeader.split(' ')[1];
if (!token) return res.sendStatus(401);
jwt.verify(token, secret, (err, user) => {
if (err) return res.sendStatus(403);
req.user = user; // Attach user to request
next();
});
};
Best Practices for jwt npm Security
To maintain a secure jwt authentication flow in 2026, follow these rules:
- Never expose the secret: Store your key in environment variables.
- Use strong algorithms: Prefer
RS256(asymmetric) for high-security needs, orHS256for simpler apps. - Validate claims: Always check the issuer and expiration to prevent replay attacks.
- Keep payloads lean: Do not put sensitive data like passwords in the jwt payload, as anyone can decode jwt tokens using a jwt debugger
jwt npm: Implementing json web tokens with the jsonwebtoken npm package
Integrating json web tokens is a standard for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. In a modern node.js application, building a robust jwt authentication system is straightforward thanks to the jsonwebtoken npm package. This guide will walk you through how to generate json web tokens, decode jwt tokens, and manage secure access using the most popular npm package in the nodejs ecosystem.
What is jwt and Why Use the jsonwebtoken npm package?
A jwt (JSON Web Token) is a compact, URL-safe means of representing claims. When you implement jwt npm solutions, you benefit from:
- Stateless Authentication: No session storage is needed on the server, making your nodejs app highly scalable.
- Secure Implementation: Digital signatures ensure jwt tokens cannot be tampered with.
- Standardized Workflow: Using the jsonwebtoken package allows for consistent jwt verify and jwt sign operations across your node js environment.
Step 1: Install the jsonwebtoken npm Package
To begin your implementation, initialize your project and use npm to fetch the necessary library.
Bash
npm init -y
npm install jsonwebtoken
The jsonwebtoken npm package is the “gold standard” for jwt authentication in node js, providing built-in support for various algorithms and issuer validation.
Step 2: How to jwt sign and generate json web tokens
The jwt sign method is used to create a new token. You need a jwt payload (the data), a secret key, and optional settings like the signing algorithms.
JavaScript
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const secret = process.env.JWT_SECRET || 'your_super_secret_key';
const payload = { userId: '12345', user: 'john_doe' };
// Use jwt sign to create the token
const token = jwt.sign(payload, secret, { expiresIn: '1h', algorithm: 'HS256' });
console.log('Generated JWT:', token);
When you sign a token, you are effectively creating a secure “passport” for the user that the node.js application can later verify.
Step 3: jwt verify and validating jwts
When a request comes in, your server must verify the token to ensure it is valid and hasn’t expired. This involves checking the signature against your secret key.
JavaScript
jwt.verify(token, secret, (err, decoded) => {
if (err) {
return console.error('Verification failed:', err.message);
}
// The decoded payload contains the original user data
console.log('Decoded Payload:', decoded);
});
Using jwt verify ensures that only authorized users can access protected resources. If you ever need to inspect a token’s contents manually during development, a jwt debugger like jwt.io is an essential tool.
Step 4: Implementing jwt authentication as express middleware
In a real-world node js app, you typically validate jwt tokens via express middleware. This intercepts the request, checks the header, and processes the decoded data before reaching the final route.
JavaScript
const authenticateToken = (req, res, next) => {
const authHeader = req.headers['authorization'];
const token = authHeader && authHeader.split(' ')[1];
if (!token) return res.sendStatus(401);
jwt.verify(token, secret, (err, user) => {
if (err) return res.sendStatus(403);
req.user = user; // Attach user to request
next();
});
};
Best Practices for jwt npm Security
To maintain a secure jwt authentication flow in 2026, follow these rules:
- Never expose the secret: Store your key in environment variables.
- Use strong algorithms: Prefer
RS256(asymmetric) for high-security needs, orHS256for simpler apps. - Validate claims: Always check the issuer and expiration to prevent replay attacks.
- Keep payloads lean: Do not put sensitive data like passwords in the jwt payload, as anyone can decode jwt tokens using a jwt debugger
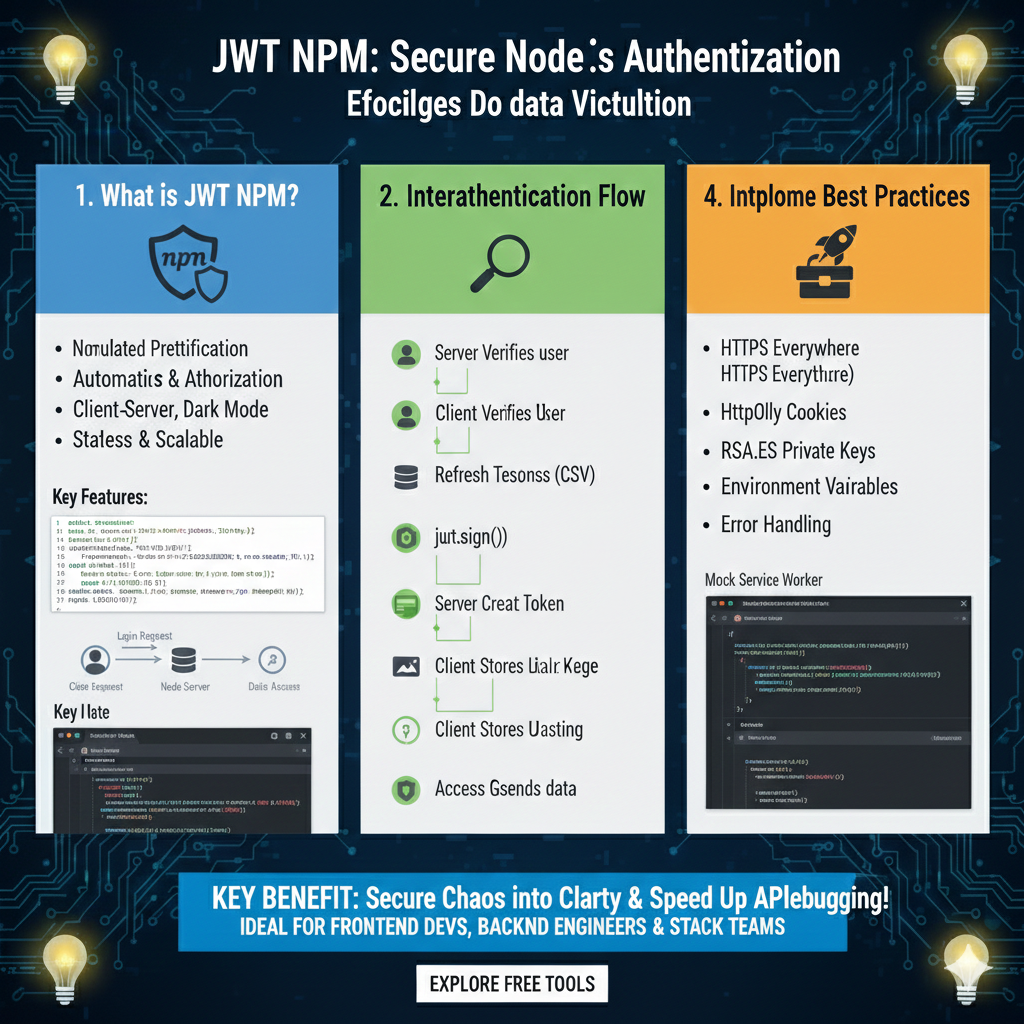
The infographic titled “JWT NPM: Secure Node.js Authentication” provides a technical blueprint for implementing token-based security within Node.js environments.
🔒 Securing Node.js Applications with JWT NPM
This guide explores the foundational concepts of JSON Web Tokens (JWT) in the npm ecosystem, the interactive authentication flow, and critical security best practices:
1. What is JWT NPM? (Blue)
This module introduces the core characteristics and key features of using JWT libraries via npm:
- Core Attributes: Provides Stateless & Scalable authentication that supports Client-Server interactions and automated authorization.
- User Interface: Supports developer-friendly features like Dark Mode and automated prettification of code.
- Key Features: Displays code snippets for handling login requests where a Client Request is sent to a Node Server for Data Access.
2. Interactive Authentication Flow (Green)
This section illustrates the step-by-step lifecycle of a secure user session:
- Verification: The process begins with the Server Verifying the user and the Client Verifying the User.
- Token Creation: Utilizes the
jwt.sign()function to enable the Server to Create a Token. - Storage & Access: The Client Stores the token and uses it to Access Goods/Data in subsequent requests.
- Session Management: Includes a mechanism for Refresh Tokens to maintain persistent security.
3. Implementation Best Practices (Orange)
The final pillar details industry-standard security measures for professional deployments:
- Network & Cookies: Mandates HTTPS Everywhere and the use of HttpOnly Cookies to protect against interception and XSS attacks.
- Cryptographic Security: Recommends using RSA Private Keys for signing and robust Error Handling protocols.
- Environment Management: Emphasizes the use of Environment Variables to protect sensitive secrets.
- Testing: Suggests integration with tools like Mock Service Worker for reliable API testing.
learn for more knowledge
Mykeywordrank-> Search for SEO: The Ultimate Guide to Keyword Research and SEO Site Checkup – keyword rank checker
Json Parser ->How to Effectively Use a JSON Parser API: A Comprehensive Guide – json parse
Json Compare ->compare json online free: Master json compare online with the Best json compare tool and online json Resources – online json comparator
Fake Json –>fake api jwt json server: Create a free fake rest api with jwt authentication – fake api