Introduction to json web tokens and Security
JSON Web Tokens (jwts) have become an industry standard (rfc 7519) for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. While the entire token is crucial, the jwt header, often overlooked, plays a fundamental role in jwt processing. Understanding the jwt structure is key to building an efficient api and safeguarding access.
Understanding the JWT Structure and JOSE Header
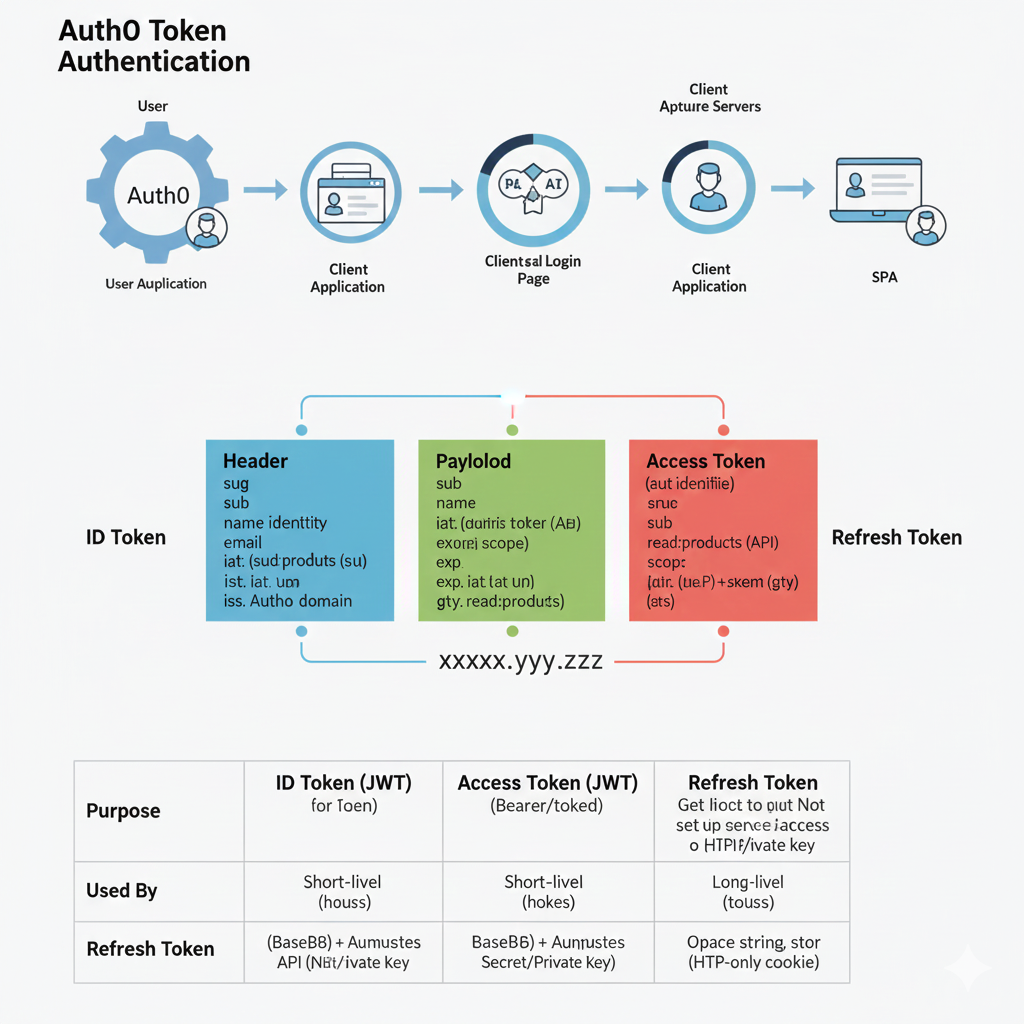
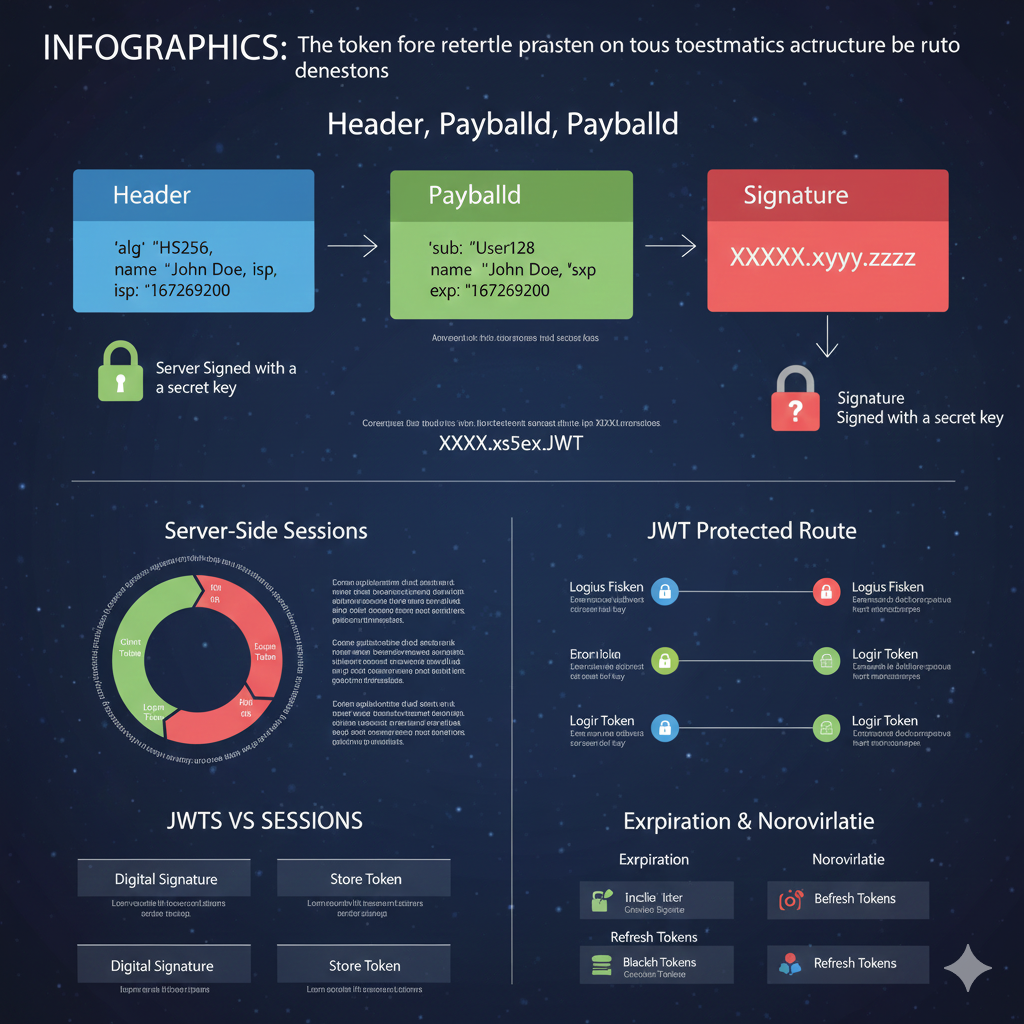
A jwt token is composed of three parts separated by dots (.): the header, the payload, and the signature. The header is technically referred to as the JOSE Header (JSON Object Signing and Encryption). It provides metadata about the signed jwt or encrypted jwt, primarily specifying the token type and the cryptographic algorithms used.
Components of the JWT Header
The header is a Base64Url encoded JSON object. When decoded, it typically contains:
- alg (Algorithm): Specifies the cryptographic algorithm, such as sha-256 (HS256) or RS256.
- typ (Type): Declares the token type, which is usually “JWT”.
Note: An unsecured jwt may have the algorithm set to “none”, but this is a major security risk in production environments.
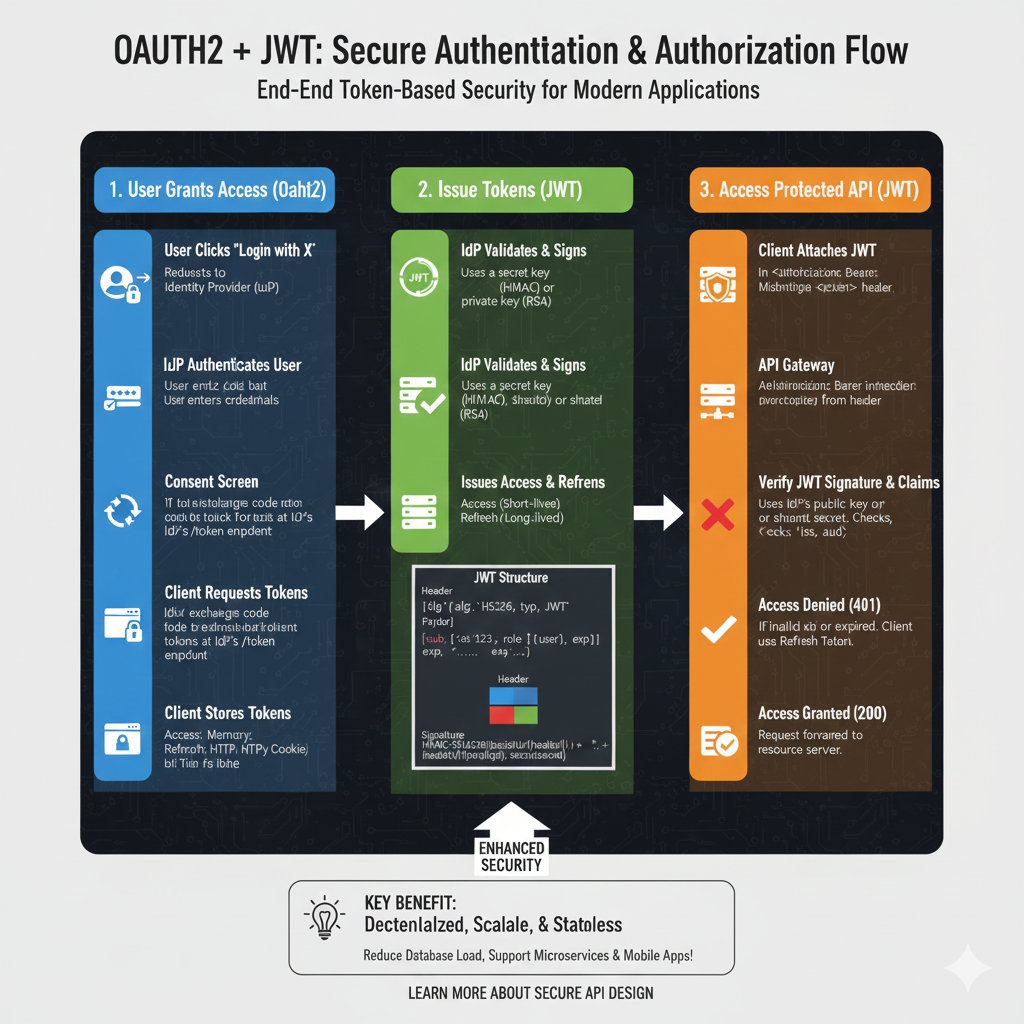
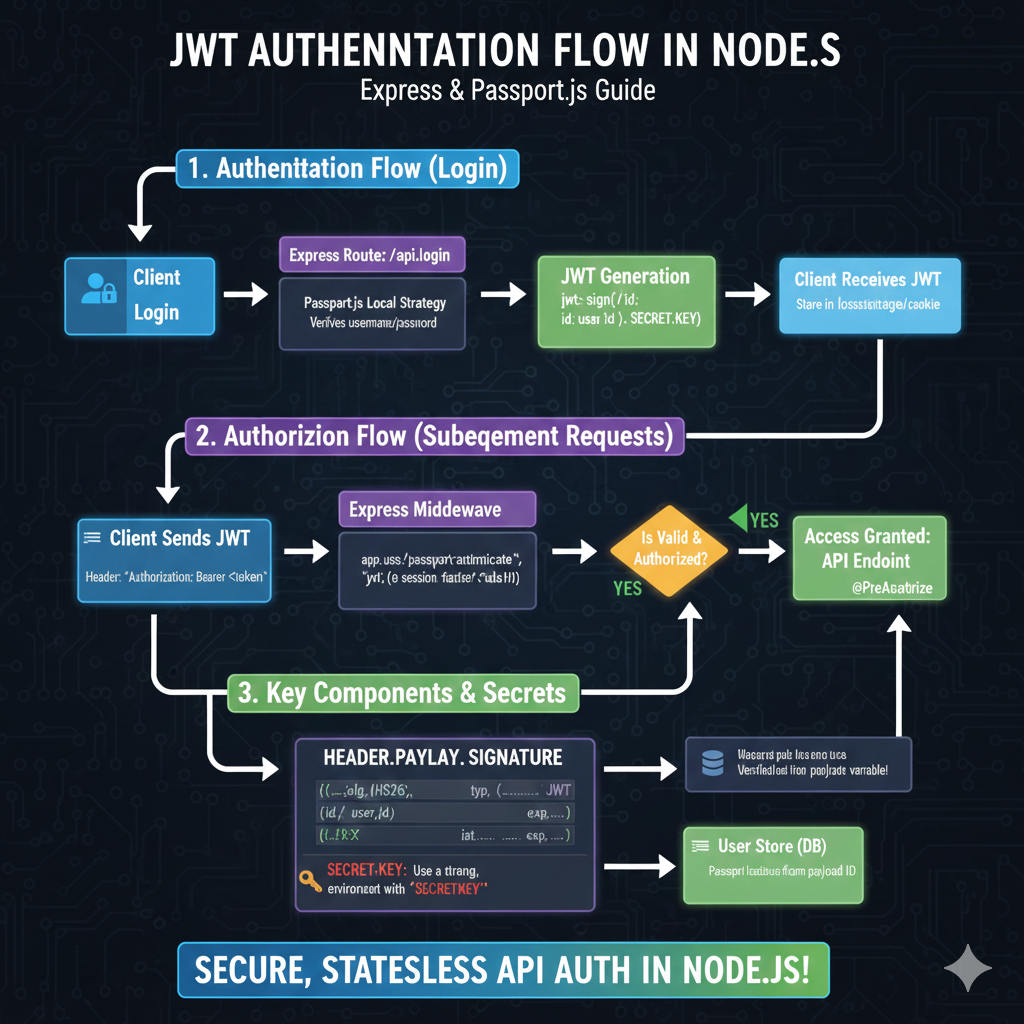
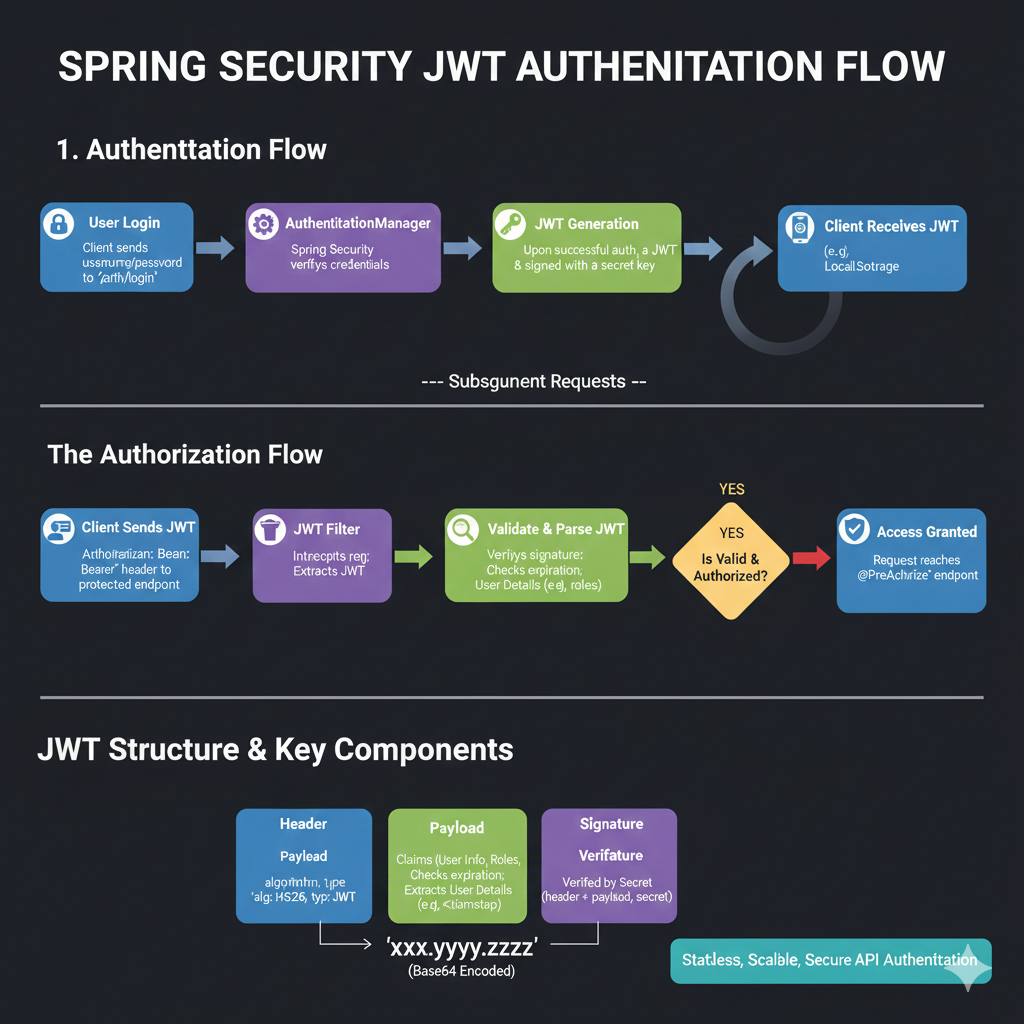
How the Header Payload and Signature Work Together
In the standard jwt structure, the header and payload are encoded separately and then combined to create the signature (often referred to as a jws or JSON Web Signature).
- Header: Defines the sha algorithm.
- Payload: Contains the claims (user data, permissions, etc.).
- Signature: Created by the server using a secret key to ensure the web token hasn’t been tampered with.
When a client sends a request header, specifically an authorization header with a bearer token, the server immediately parses the jwt header to determine how to verify the rest of the token.
JWT Processing in the Authorization Header
For most oauth and api implementations, the jwt token is passed in the request header as follows:
Authorization: Bearer <token>
The server performs the following validation steps:
- Algorithm Negotiation: It reads the alg field to know which key to use for the signature.
- Type Verification: It confirms the token type matches expectations.
- Integrity Check: It re-calculates the signature using the header payload and its own secret key.
Best Practices for JWTs and Access Control
To ensure robust security when working with json web tokens:
- Never Trust the alg Blindly: Malicious users might change the algorithm to “none”. Always hardcode supported algorithms on your server.
- Keep it Lean: The jwt header should only contain necessary metadata for jwt processing. Avoid placing sensitive claims here.
- Use Strong Algorithms: Stick to sha-256 or higher (RS256/HS256) to ensure the signature cannot be easily cracked.
- Validate the Issuer: Always check the
issclaim in the payload alongside the header validation.
Conclusion
The jwt header is a small but mighty component of the json web token. By mastering its role within the jwt structure, developers can implement jwts more effectively, strengthening the authentication and authorization mechanisms of their applications. Whether you are building a simple api or a complex oauth identity provider, the header is your first line of defense.
The Three Pillars of a JWT Header
The graphic illustrates how the header acts as the instruction manual for the rest of the token:
1. Structure: The JWS Header (Blue)
This section defines the physical makeup of the header:
- Format: It is a JSON Object that is Base64Url encoded for transmission.
- Required Fields: Every header must include the
alg(Algorithm) field. - Optional Metadata: It can include fields like
typ(Token Type),cty(Content Type), orkid(Key ID). - Example Encoding: Raw JSON such as
{"alg": "HS256", "typ": "JWT"}is transformed into a URL-safe string likeeyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiJ9....
2. Purpose: Security (Green)
The header contains the specific parameters needed to verify the token’s authenticity:
- Algorithm Specification: The
algclaim defines which signing algorithm is used, such as symmetric HS256 or asymmetric RS256. - Key Identification: The
kidfield helps the server identify which specific key should be used for validation, which is vital for Key Rotation. - Signature Verification: This metadata is used directly by the server to verify the final signature of the JWT.
3. Role in the JWT (Orange)
This section explains how the header sits within the overall token structure:
- The First Segment: The header is always the FIRST part of the dot-separated JWT string (header.payload.signature).
- Client Transparency: While the client can read the header, it must not trust it until the signature is validated.
- Server Responsibility: The server MUST validate the
algfield to prevent “none” algorithm attacks or other tampering.

learn for more knowledge
Mykeywordrank-> small seo tool for keyword rank checking and local rank checker – keyword rank checker
json parser-> How to Parse JSON in C with jsmn parser: A Step-by-Step Guide for SEO – json parse
Json Compare ->JSON File Compare Online: The Ultimate JSON Compare Online and JSON Diff Guide for Files – online json comparator
Fake Json –>How to Easily Get dummy json data api Your API Testing and Development – fake api